In the digital era, cloud-based applications are anticipated to rule the technological landscape. By 2021, more than 94% of workload and computer operations will be housed in the cloud, predicts Cisco Cloud. Because of benefits like scalability, increased productivity, cheaper prices for traffic, and much lower equipment expenses, cloud computing is becoming more and more popular in eCommerce and other commercial sectors.
Do you require a list of numbers? According to over 47% of firms, switching to the cloud may be driven mostly by cost savings.
You might assume that something as fantastic as cloud computing would be simple to use whenever you wanted. However, just like every other technology, cloud computing has advantages and disadvantages. For companies or people who utilize cloud computing, there are some problems and risks.
In this blog, we’ll learn about the hazards and challenges of cloud computing, as well as strategies for lowering or avoiding these risks.
What is Cloud Computing?
A kind of computing known as cloud computing makes use of a network of remote services to provide software and hardware services over the internet. The servers handle, process, and store data, enabling users to expand or update their current infrastructure.
Without requiring users to manage or control the system, it provides on-demand resources like computing power and data storage. Several cloud service companies, including AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and many more, offer cloud computing services. These cloud service providers use a pay-as-you-go model to supply the services to customers and have servers spread out over numerous data centers around the world.
Different types of Cloud Computing Services
Are you considering switching to cloud computing and considering your options? Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Functions as a Service (FaaS), and Software as a Service are the four categories of cloud computing services (SaaS).
Businesses can manage their own networking, computing, and storing components with IaaS without having to physically manage them. PaaS provides the framework required for developers to create original applications. SaaS provides outside organizations with internet-connected software.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The access cloud computing service offered by a company, where other infrastructure resources are provided by a third party and are under your management. Users that use IaaS have access to networking processing power, networking, and data storage capacity.
Showing progress users access computing resources or virtual machines without having to purchase infrastructure or manage servers. These computer components are physically sourced from a variety of networks and computers dispersed throughout numerous data centers. The cloud provider oversees and manages each of them.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
The platform for cloud computing is an improved version of IaaS. PaaS offers options for platforms for computing and solution stacks in addition to services for the IT infrastructure. PaaS is a type of cloud computing that gives developers access to infrastructure for the creation of unique applications. Software developers can create unique online applications using Platform as a Service without having to worry about data management, storage, or service.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
IaaS and PaaS services are special cloud computing service. Cloud computing service SaaS provides application-specific services like CRM, business analytics, and marketing automation specifically suited to the needs of businesses. SaaS is a cloud computing service that offers clients on-demand access to web-based software. SaaS providers offer users access to a fully functional application with an Internet-based browser-based interface.
Function as a service (FaaS)
Understand Functions as Service in the context of serverless computing, the most well-known technical phrase related to FaaS servers. A method known as “cloud computing” frees developers from having to manage servers and make low-level decisions about infrastructure. The application architect need not worry about the allocation of resources. The cloud service provider does it.
The Key Issues within Cloud Computing
To develop cloud-based software you can choose anyone from the two. Build an application based on third-party cloud solutions or run your firm as a cloud-based applications service provider (SaaS, IaaS, FaaS, and PaaS). To give your service a host and give its users access to a cloud-based applications network, you should consider these difficulties in the first scenario as the security of your service, data processing logic, and hardware.
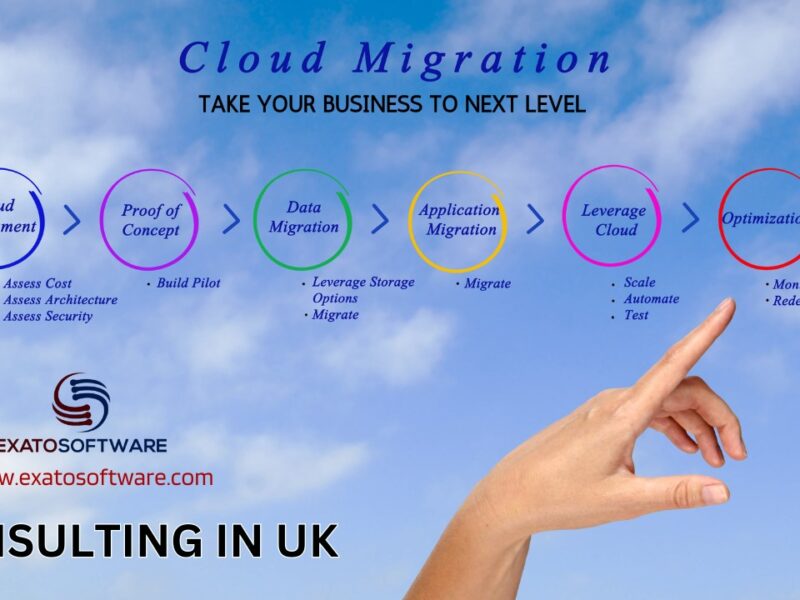
Cloud Migration
If a business decides to use cloud computing and relocate there, relocating all of its outdated or traditional apps there will be quite challenging. The entire procedure could take a lot of time and money, and they may not know how to deal with seasoned cloud service providers who have been in business for a while.
Similar to switching between cloud providers, they will have to start from scratch and are unsure of what the new provider would do to supply them with the services they require. They have to deal with difficulties including slow troubleshooting times, security problems, app complexity, downtime, and other problems, in addition to prices and other difficulties. This is a serious issue for both businesses and customers. It might ultimately lead to a bad user experience, which would have a number of negative effects on the company.
Reliability
Service interruptions cause enrollment problems, most Cloud developers are attempting to improve their uptimes. Smaller cloud-based application service providers are typically more susceptible to disruptions. Even with technological advancements and well-designed backups, this problem persists.
Business systems for Cloud computing include different levels of redundancy. To avoid interruptions, they are also creating backup plans and disaster recovery systems. Assistance of reputable cloud computing suppliers is advisable.
Multi-Cloud Infrastructure
Businesses have used multi-cloud methods. In this one organization signs up for the services of several service providers and links them all to another, in an effort to cut expenses.
Business data shared with a number of service providers raises the chances of data security breaches. Cloud deployment for big businesses is usually complicated.
Security and Privacy
The largest issue in the technological world is “Data security and Privacy”. The acceptance of cloud computing hinges on how it addresses the privacy and data security concerns of businesses. Knowledge that critical company data is not the firm’s firewall creates serious worries for businesses.
Attacks on cloud infrastructure pose a significant threat to those who had stored sensitive customer data as cybersecurity crime rates rise. To prevent likely security breaches, cloud service providers need to provide reliable security software, secure systems, and other security technologies. They will also need to give SLAs that ensure the protection of the security of data and privacy.
Efficiency and the Cost for Bandwidth
Monitor and assess regularly the Key Performance Indicators. Take required action to address any potential or significant departures from the intended course of action. Although businesses can cut back on the cost of their technology, they must still pay for broadband or high-speed internet. However, the cost of bandwidth may be minimal for smaller applications, it is dramatically high for data-intensive apps.
The network should transfer large and complex data quickly and efficiently. Cloud providers shall make high-performance and Continuous apps available for use in their cloud. In addition, before introducing any new technology, firms must assess the TCO.
The Key Takeaway
There are many futuristic benefits of cloud computing those also entail a great deal of danger and problems for enterprises. It is critical to comprehend the difficulties that can occur if you choose to move your workload to the cloud.
It will help you plan and successfully navigate those challenges. It’s important to take the initial step towards the cloud without incident in addition to lowering the stress.