Cloud computing isn’t anything new to the business. Nearly 98% of businesses have their hardware servers on-premises to manage their IT infrastructure. However, the pandemic has caused some changes. Today, companies consider cloud migration and staying away from older systems to ensure that their business is uninterrupted. A survey from Flexera revealed that more than half of organizations believe, cloud migration can help to improve business sales and productivity.
The cloud migration process can be overwhelming. There are concerns about stability costs, stability, and security issues. For many, the successful migration of cloud services reduces cost, enhances scalability and drastically reduces the likelihood of cyber-attacks which could cripple your business. Let’s get started to find out what cloud migration is? How difficult is it to complete? What are the advantages of cloud migration?
What is Cloud Migration?
It is the procedure of moving digital business processes to the cloud. Cloud migration can be described as similar to a physical move. It involves moving information, applications or IT systems from certain data centers to different data centers. Like moving from one office to a larger one, cloud migration takes some planning. However it is typically worthwhile, as it results in lower costs and more flexibility.
In simple terms, cloud migration is defined as the process of migrating on-premises infrastructure to the cloud. Instead, the term could describe a migration from one cloud and another.
Cloud Service Models
There are 3 major cloud service models designed to meet the specific requirements of business. Also to create a cloud-based environment as appropriate as it can be.
- Software as a service (SaaS): Software accessible through vendors on the internet. Salesforce, Dropbox, Slack and MailChimp are just a few examples of SaaS.
- Platform as a service (PaaS): Platforms that provide the tools required to develop applications. A few examples are AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku and other Microsoft Azure services.
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS): Cloud-based platforms that use a pay-as-you-go method to offer computing facilities. For example, AWS EC2, Rackspace, Digital Ocean and Google Compute Engine are some examples of IaaS.
- On-Premises: Hardware and software installed at the company’s office or datacenter.
Cloud Deployment Models
In simple words, cloud deployment is how software is made accessible. This, in turn, impacts who has access to the cloud’s data and how.
There are three major models:
- Public Cloud: This cloud computing model makes digital assets in the cloud accessible to the public via the internet. Google, Facebook and LinkedIn are all examples of publicly available services. These cloud services are usually available for free to customers or on monthly-fee basis (i.e., PaaS, SaaS).
- Private Cloud: This type of cloud serves to one specific organization and cannot be accessed by any outsider or third-part.
- Hybrid Cloud: It is possible to discern by the name it is a mix of infrastructure on-premises with cloud computing, including public cloud and private cloud. Large corporations typically use it to store important data in the private cloud and various support-related services in the public cloud.
What are Common Cloud Migration Challenges?
The process of moving cloud resources can be complicated and dangerous. Here are a few most significant challenges many companies face when they migrate their resources to cloud computing.
Lack of Strategy
Many businesses begin their journey to cloud computing without giving enough time and effort to their cloud strategy. The successful adoption of cloud technology and implementation requires a thorough plan of action from beginning to end. Every dataset and application might have its demands and requirements that require a different approach for cloud migration. The company must develop a clearly defined reason for every one of the workloads it transfers into the cloud.
Cost Management
During migration, many organizations haven’t established clear KPIs to better understand how much they will invest or save upon transition. This makes it hard to determine if the migration was successful from a financial perspective. Cloud environments are ever-changing, and costs change quickly as new services are embraced and the use of applications increases.
Vendor Lock-In
Lock-in by vendors is a typical issue for adopting cloud technology. Cloud providers provide a wide array of services, but they are not all expanded to different cloud providers. Transferring the workload from one provider to the next is a long and expensive process. Many companies begin using cloud services and then find it difficult to change providers, if the service they’re using currently doesn’t meet their business requirements.
Data Security and Compliance
One of the main challenges to cloud migration is protection and conformity. Cloud solutions employ the model of shared responsibility. They assume responsibility for the security of their infrastructure, and the user is accountable for protecting their data and their workloads. While the cloud service can provide security features, it is your company’s responsibility to ensure that they are properly configured. Ensure that all applications and services come with the proper security safeguards. The process of migration itself can pose a security risk. Sometimes moving large amounts of data that may be sensitive. Also setting access controls for programs across multiple environments, exposes users to substantial risk.
What Cloud Migration Strategy Should Enterprises Adopt?
Gartner, an important research and development company in information technology, offers five options for companies looking to move to cloud computing. Cloud strategies for migration are generally referred to by “5 R’s”.
Rehost: Rehosting, or ‘lift and shift,’ involves using infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), you can redeploy existing applications and data on your cloud servers. It’s simple and suitable for companies that aren’t accustomed to cloud-based systems. It’s also an excellent alternative for situations when it’s difficult to alter the code, and you need to move your application without compromising it.
Refactor: Companies going with refactoring the pre-existing codes and frameworks. However, their applications still run on the PaaS provider’s platform, unlike rehosting.
Revise: This strategy involves rewriting or expanding the code base before applying it through Rehosting or restructuring (see earlier).
Rebuild: “Rebuild” involves rewriting and restructuring the application from scratch on the PaaS vendor’s platform. It can be a time-demanding process, but it also lets developers use the latest features offered by PaaS providers.
Replace: Businesses also have the option to discard their existing or old applications and switch to a pre-built SaaS application from a third-party service provider.
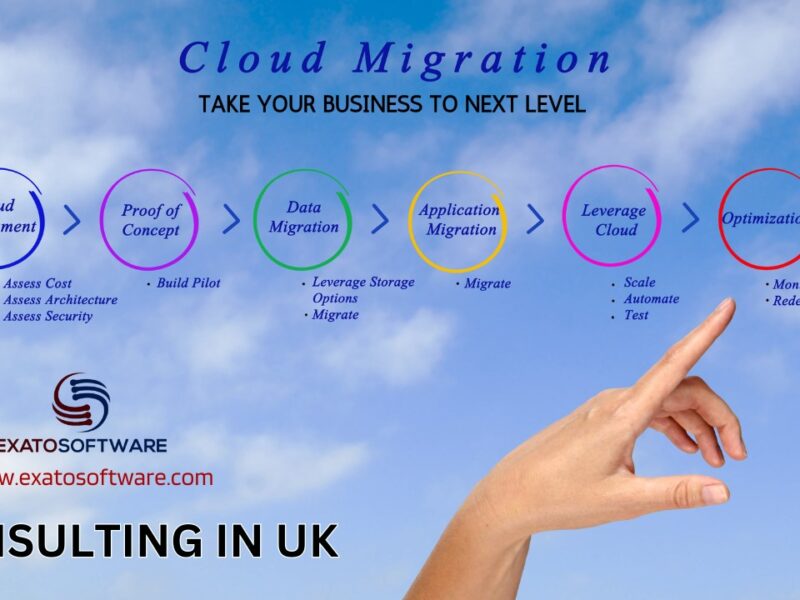
The Cloud Migration process in 4 Steps
Cloud Migration Planning
Before moving data to cloud storage, the first thing to take is to identify what purpose the Cloud’s public service will be used for. Could it be used to help in disaster recovery? Hosting business workloads completely moving to cloud computing? Or, will a hybrid approach be the best option for your application.
At this point, it’s essential to analyze your surroundings and identify the elements that will influence the migration process, such as important application data, old data, and interoperability between applications. It is also essential to assess your dependence on data. Do you have data that must be synced frequently or data compliance requirements to be met or other data that could be moved in the initial few phases of the process?
Knowing these needs will allow you to create a plan of action to use the tools you’ll require to migrate, including identifying what data must be transferred and when. Also, should the data require some scrubbing, what type of volume to be used for the destination, as well as whether you’ll require encryption of your data at rest and while in transit.
Business Case Migration
After you have identified your company’s requirements, be aware of the services provided by cloud service providers and other partners and the costs associated with them. Consider the anticipated benefits of cloud migration in three areas: operational benefits, cost savings, and improvements to the architecture.
Make a business plan for every application you want to move to the cloud. It should include the expected total cost of operation (TCO) for cloud services compared to the current TCO. Use cloud cost calculators to calculate costs using realistic assumptions, such as the quantity and type of storage, computing resources, and operating systems, types, and particular requirements for networking and performance.
Engage in conjunction with cloud services providers to understand the cost-saving options available for your cloud deployment. Cloud providers offer various pricing models and huge discounts as a condition of an ongoing engagement to cloud services (reserved plan) or commitment to a specific amount of cloud usage (savings plan). Discounts must be included in your company’s business plan to determine the actual costs of the cloud migration over time.
Cloud Data Migration Execution
After your environment is evaluated and a strategy has been drawn up, then it’s time to begin your move. The biggest challenge is to complete your move with the least interruption to your normal operations, at the least cost and in the least amount of time.
If your data is not accessible to users after an upgrade, you risk negatively impacting your business. This is the same case if you continue to update and sync your systems after completing the initial transfer. Each element of your workload must be tested to ensure it works in the new environment before moving to another component.
Additionally, you’ll need to discover a method to sync changes made to the original data source while the migration process is on. AWS and Azure offer built-in tools that assist in AWS cloud migration.
Ongoing Maintenance
Once the data is transferred to the cloud, it’s crucial to ensure that it is properly optimized and secure and accessible in the future. It is also useful to keep track of any real-time changes to the important infrastructure and anticipate the likelihood of workload conflicts.
With real-time monitoring, you should also evaluate the security of your data in transit to ensure that your work within your new setting complies with the requirements of compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
Another thing to consider is to meet the regular benchmarks for availability and performance to ensure that you meet your Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) goals are not affected should they change.
Benefits of Migrating your Application to the Cloud
If you’re aware of the available options and what you can do, it’s time to figure out how to gain by cloud migration.
Allow Digital Transformation
Many companies are going through a digital transformation to get incremental value from existing assets. With the recent innovations in cloud computing, executives can digitize more of their core functions such as SAP, CRM the data analysis, and many more.
Anyone who migrates from outdated technologies could improve the productivity of their workforces, develop new ideas and discover new revenue sources compared to their competitors. Once in the cloud, there are limitless possibilities.
Scalability
With cloud-based workloads, it is possible to respond quickly to the demands of peak times and decrease capacity when necessary. This is all done automatically and does not require much time or effort. If you use on-premises hosting, you’ll require additional equipment and set it up to expand capacity. However, once a load peak is over, you’ll need to cover the cost of redundant resources it uses.
Yedpay is a payment service that has decided to move to the cloud following problems with their data centres. There was no need for large IT investment and personnel to maintain physical infrastructure. The company was able to cut expenses by 40%.
Enables Remote Working
In addition to reducing the carbon footprint, cloud-based companies enable their workers to connect to work from any place. When COVID-19 was first introduced, Cloud-powered businesses were the best at adapting to the government’s mandated homeworking. Since it has now been established as a viable working method and a viable option for employees, they are likely to seek the flexibility of their managers more than they have ever. Making the switch to the cloud could be essential in keeping and attracting top employees.
Reliability
There are examples where cloud deployments are smooth. There may be issues with the hardware or downtime. But cloud migration can effectively decrease downtimes and reduce the risk of data loss shortly.
Cloud providers typically offer service-level agreements which guarantee 99% uptime. In addition, they are responsible for disaster recovery and backups which can help save time for your staff.
The Under Armour Connected Fitness platform was faced with a reliability issue. The company was operating two data centres and, when problems occurred in the first one, it would result in outages. The company then shifted to cloud computing, which solved the problem.
Time-Saving
Not only is it simpler than ever before to move your existing systems to the Cloud computing system, but doing this will reduce time and effort in installing new applications or training to your company.
With no data centres to frequently restore, backup, and back up, your IT teams have more time to focus on the day-to-day running of your company. In addition, Cloud-based tools for collaboration enable collaboration and communication much easier than ever. This means more times used by more people, making you more productive.
Rapid Implementation
From a growth perspective for business, cloud computing provides endless opportunities for companies. Also, it is a source of the speed of digital advancement. With the flexibility of technology offered by cloud-based providers developers, you can streamline and speed up processes.
Capital One back of the US managed to reduce the mobile app development build time. They did it by moving their services to cloud.
Capital One, one of the biggest U.S. banks, managed to cut down the mobile app development environment’s build time from months to just a few minutes following its move to the cloud.
Availability
Cloud computing allows you and your staff to access your applications from any part of the globe at any point. It allows companies to offer employees a flexible work schedule and a seamless transition to remote working.
The Key Takeaway
One thing is certain that almost every business driven by technology must have at least a Cloud migration plan. If you don’t, then why wouldn’t you? The need to migrate from outdated software is the right step to take. It is a must-have to ensure continuity of business and an investment that will pay promptly for many firms.